Health applications are mobile and web apps that offer health-related services. They are accessible to patients both at home and on-the-go. For the past few years, healthcare app development has grown at an unprecedented speed due to numerous reasons, the main one being the pandemic.
While it has certainly been used for many years, it’s been on an exponential rise due to the pandemic. So much so that the CDC saw a 154% increase in telemedicine doctor visits during March 2020 as compared to the number of visits at the same time the year before.
Healthcare application development serves different purposes for physicians and other medical professionals. It helps in monitoring, patient tracking, staff management, appointment scheduling etc. For patients- health apps are used to track wellbeing, seek medical recommendations and book appointments.
In this blog post we will go over the following:
- What is healthcare app development?
- The benefits of healthcare apps
- The difference between a health app and a medical app
- Examples of both Medical and Health apps
- Different types of health apps available
- The necessary steps to build a health app and how to create a medical app
What is Healthcare App Development?
It is the process by which an app is developed, either for mobile devices or the web, with the intent of helping users effectively manage their medical conditions, track health stats, fitness goals, hospital visits, insurance claims, among others. This can include telemedicine apps, patient and physician portals for prescription & appointment management, consumer health applications and more.
Developing these solutions for the healthcare industry is an impactful way to make the lives of physicians and patients easier by providing a wide range of improvements that tech can bring to different medical services.
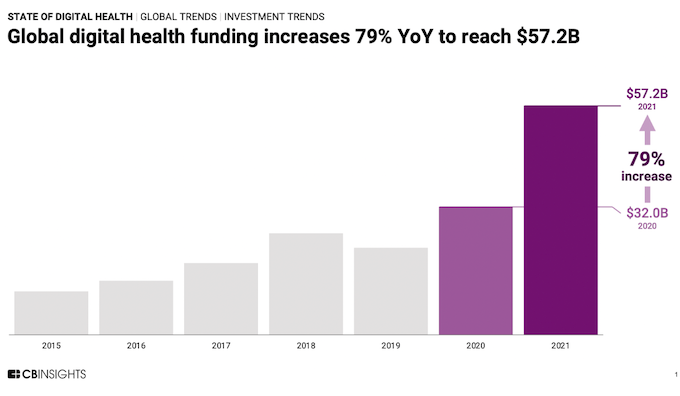
According to CB Insights digital health startups pulled in a record-breaking $57.2B in funding in 2021, which is up 79% from 2020. This was fueled by the growing need to provide digital solutions and delivery models to patients during the pandemic. These companies are also scaling at a higher rate. Even though we can largely say the public health emergency is over and in person care has resumed, digital health has become part of our everyday lives. Telemedicine will continue to grow, and it is expected that many new platforms and technologies will pop up to improve patient experience.
Benefits of Healthcare Apps
Technology has been driving a revolution in health care, from mobile apps, software that facilitates decision making for doctors, to artificial intelligence.
The main benefits include:
- lowering the cost of healthcare
- helping patients monitor and manage chronic conditions
- making medicine more tailored to individual needs
- Facilitating access
- Reducing overall cost
These benefits are not only for patients but also healthcare providers and give patients greater control over their health. Digital health tools could potentially help providers diagnose diseases earlier and help people ease their symptoms.
Health and medical apps also help to reduce overall healthcare costs for both patients and providers. According to the IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science, it was concluded that the use of health applications and wearable devices could possibly save the U.S. healthcare system $7 billion per year. That particular analysis centered on the impact of consumer health apps and studied those such as diabetes care and prevention, asthma, cardiac rehabilitation, and pulmonary rehabilitation, but they also came to the conclusion that if health apps were used for all diseases the healthcare system could potentially actually save $46 billion in annual cost.
Another important area where health and medical apps make a difference is the actual delivery of healthcare to patients. As a result of being able to be accessible to patients both at home and on-the-go it has greatly improved their accessibility and the speed of delivery. It has brought specialists to remote areas where as before patients had to travel long distances to metropolitan cities to be able to access this type of care. Digital health has greatly reduced wait times for appointments and also travel times to the actual offices.
The ease with which healthcare providers can collect and store information is an important benefit provided by medical and health apps. They make it easier for physicians to collect and retrieve information from patients and have everything handy in their electronic health records (EHR). Healthcare providers who use these apps allow patients and physicians to access patient information, medical history, vital signs tracking, and also lab results and interpretations of these. For healthcare providers, the exchange of electronic health records (EHR) is very important. Making sure that records can be exchanged between different providers and with patients safely is the primary concern. The security and privacy of these records is key.
Patient medical records and information is stored in an Electronic Health Record (EHR or sometimes referred to as EMR) which is a type of record-keeping system for both healthcare providers and patients. The EHR was developed to create a standardized system for storing records, which includes medical history, demographics, healthcare information, diagnostic images and laboratory test results.
What is the Difference Between a Health App and a Medical App?
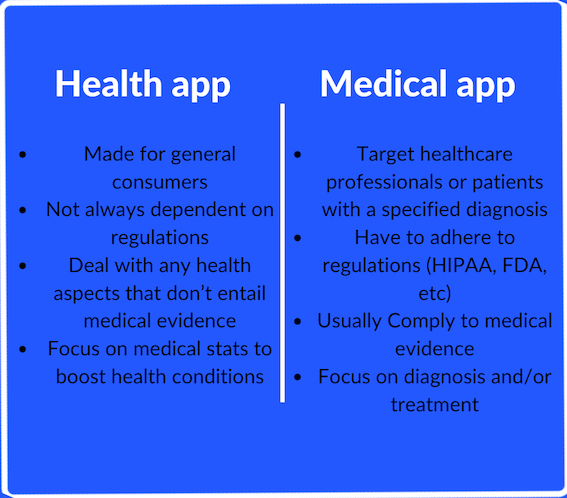
When it comes to the differences between a health app and a medical app there’s a lot of confusion on the subject. Many people think they're the same thing and refer to anything related to medtech as healthtech or a health app. The two fields have some similarities such as they both primarily target the healthcare market (such as providers, pharma, patients, government healthcare services, and other healthcare industry players), but they have a few key differences.
Health app
A health application could be used in the healthcare setting or it could be a consumer app for the end user to track and manage their own health. This is also referred to as digital health, which is the use of technology for a better delivery and/or utilization of care. Health applications are mostly about personal health, meaning patients engage with their personal health. It’s basically everything that happens outside of the hospital, like telemedicine and personal monitoring. Healthtech is more about prevention and monitoring rather than treatment.
Health applications operate with various other technologies, such as databases, mobile devices, and wearables. An example of this would be wearables that can track patients’ steps, blood sugar, heart rate, and automatically send that information to the health app on their phone. The app then analyzes the healthy habits of the user and gives recommendations and feedback accordingly. According to the WHO the definition of health technology is the application of organized knowledge and skills in the form of medicines, medical devices, vaccines, procedures and systems developed to solve a health problem and improve quality of life.
Medical app
Medical applications are more inclined towards cure-based systems which are usually used in hospitals. It’s commonly used for patient care, diagnosis, treatment, and improvement of patient health. We would even include in this category physician prescribed mobile applications. There are a great deal of mobile applications that need a physician’s prescription in order to download them. For example BlueStar —which is an app that helps people with type 2 diabetes –the most common form– by notifying them when it’s time to check their blood sugar levels. The necessary steps to create a medical app and a health app are largely the same.
Medical apps can be connected to or integrated with equipment, devices, machines, software, and other tools. These types of apps have a more regulated path to market since they may have a severe effect on people’s health. They are also more heavily regulated to protect patients’ privacy since there is a constant flow of information between either the patient and healthcare providers or among healthcare providers. The main regulation is HIPAA compliance, which is a federal law that requires the creation of national standards to protect sensitive patient health information from being disclosed without the patient’s consent or knowledge. To learn more about this read our dedicated post on HIPAA compliance.
For medical devices, in some cases, they need to have FDA clearance in order to market them to consumers. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s Center for Devices and Radiological Health (CDRH) is the one responsible for regulating firms who manufacture, repackage, relabel, and/or import medical devices sold in the United States. The approval process is intended to provide consumers with assurance that once a medical device reaches the marketplace it is safe and effective in its intended use.
According to the Federal Food Drug and Cosmetics Act, a device is “an instrument, apparatus, implement, machine, contrivance, implant or an in vitro reagent” that meets 3 conditions:
1) It is recognized in the official National Formulary or the U.S. Pharmacopeia;
2) It is intended for use in the diagnosis of disease or other conditions, or the cure, mitigation, treatment, or prevention of disease; or
3) It is intended to affect the structure or function of the body of humans.
To learn more about how to navigate the FDA approval or clearance process check out our dedicated post.
Examples of Medical Apps
Some popular medtech companies to follow are:
Zeit Medical
A smart headband that constantly monitors the electrical activity of your brain and gets help immediately, should the person need it. It provides peace of mind to those affected by neurological injury and empowers physicians to diagnose and treat with precision.
Bloomllife
Bloomlife is a healthcare startup developing clinically certified wearable medical devices for pregnant women to improve birth outcomes. Bloomlife has identified that there are significant and underrated challenges in prenatal healthcare, and have created a wearable solution with data analytics to help doctors predict and pre-empt any pregnancy complications.
FibriCheck
FibriCheck is a medically certified screening and monitoring app, on prescription which is used to detect irregular heart rhythms, including atrial fibrillation. This medical software solution requires the user to place their finger on the camera of the smartphone to measure the cardiac rhythm easily. The data is recorded and shared with a medical professional to increase the efficiency of diagnosis and prognosis.
4C Medical
A Medical startup that has created a device that they believe to be a solution to invasive surgeries for structural heart disease. The AltaValve device is designed to minimize the risks associated with transcatheter mitral valve replacement.
Encellin
Encellin is a MedTech startup based in San Francisco, pioneering a novel thin-film cell encapsulation device for cell-based therapeutics. Behind Encellin’s medical innovations is a team of dedicated scientists working on the advancement of next-generation therapies. Encellin’s mission is to help alleviate the suffering of chronic patients, beginning with Type 1 diabetes as its primary focus.
Types of health apps
Telehealth
This refers to mobile platforms that connect physicians with their patients. We develop telehealth platforms that allow doctors to exchange text, image, audio and video messages; and can make audio and video calls. These types of apps are bringing us fast, efficient, and affordable medical care. They are slowly disrupting healthcare systems across the world and are driving the search for more universal, accessible healthcare services. They are improving access to healthcare for millions of patients.
Patient and Physician Portals
These types of applications offer interoperability and secure care coordination to ease clinical communication between providers and patients and improve workflows. They allow providers to effectively streamline communication between patients, other providers, and their caregivers and allows for 24/7 management of a patient’s condition along with the ability to personalize healthcare per patient.
Consumer applications
They allow individual consumers to monitor and track their daily physical activities. We create both mobile and wearable versions worn to monitor and transmit key health indicators in real time such as physical movement, oxygen levels, blood pressure, fall detection, and many more. Consumer applications are a great way to help bring health to the user’s fingertips.
All in all the main difference between health and medical apps lies in the way they are implemented through different forms of technology. Regarding health apps they are implemented through wearables, applications, or databases, whereas medical applications are implemented through medical equipment, prosthesis, and tools. Although, there’s one aspect where they are similar: both types connect technology with healthcare.
Examples of Health apps
The number of consumer digital health apps has experienced an exponential growth. It is reported that there are over 350,000 digital health apps available to consumers. Some examples are:
CardMedic is a web and mobile app designed to improve communication between healthcare staff and patients, across any barrier – whether that’s visual, hearing or cognitive impairment, a language barrier, or PPE (personal protective equipment). It replicates conversations around common healthcare topics with simple questions and explanations to guide the clinical interaction.
This mobile app is a flexible food and symptom diary that provides help to identify trigger foods in your diet. mySymptoms can track food, bowel health, stress, sleep, mood, periods, medications and symptoms to gain insights into your digestive health and well-being.
A free, secure messenger mobile and web app designed for individuals and teams in healthcare. It meets the highest security standards for data processing in healthcare. They provide a suite of tools designed to help healthcare professionals further anonymise and protect any patient data exchanged.
They provide personalized healthcare at an affordable price. They have an online medical team and pharmacy that provides care when and where you need it. You can receive medical care with either an online doctor or nurse practitioner and they deliver most prescription Rx in discreet packaging with fast and convenient shipping.
March is a period tracker, ovulation calculator and pregnancy tracker. It’s geared towards improving women’s reproductive health. They also have a sensor wearable that learns the pattern of your period pains and reduces them with pulses and heat.
Steps to Build a Health App
There isn’t a perfect step by step guide to follow for healthcare app development, as it largely depends on many things.
These are some of the common steps we take in the product development lifecycle.
- Product Ideation and Strategy: This is where we carefully analyze your business model and ask strategic questions to help you shape your idea into the right product for your market. We analyze the client’s needs and elicit the app requirements, define the necessary app features, build a healthcare app project scope, and delivery plan.
- UX/UI design: We thoroughly explore the physician and patient journeys to create the perfect user experience as well as design an attractive and appealing user interface. When it comes to healthcare application development design, user experience is key. It's critical to take a user-first approach to application design. Whether the end users are patients or physicians, the goal is to ensure digital tools are easy to use and that they improve people’s lives. Digital products in the health and wellbeing space carry unique and important challenges. The design of the app must be as clear and easy to use as possible, any room for confusion can have serious consequences when it comes to users’ health (e.g. taking the wrong medication, inputting wrong health data for a provider, etc). We need to make sure to find the right balance between functionality and design.
- Front end and Back end development: To create the user and the server side of the application based on an iterative approach (the development process is split into sprints). The development timeline is something that largely depends on what you have in mind for your product. Such as what type of features you want it to have, if you want to build it natively in iOS and Android, or use a cross platform framework. An average project for us could vary between 2 and 6 months.
- Testing: We use scrum methodology for our processes and that means testing frequently. We have processes for testing and quality assurance that we’ve honed with our years of experience. We use automated testing to accelerate workflows and magnify the efficiency of the quality assurance process. Our code is peer reviewed for finding defects, better solutions and overall achieving better code quality.
It’s also important to take into account how the agency you might engage works and what their process is like. For example, at Hattrick we work with Scrum. Scrum is the most popular agile methodology. It lays out a framework and collaboration agreement that consistently produces valuable output. Based on our experience, when practiced properly, Scrum is a proven way of cultivating teamwork that produces products that have real impact. Scrum helps us work together effectively. It empowers us to learn through experience, to self organize while solving problems, and to reflect on our wins and losses throughout the process in order to continuously improve and deliver results.
We work in two week sprints where we, along with the client, create a product backlog, which is a prioritized list of features or tasks. With this in mind we have an all team meeting to plan the items for the sprint and create a sprint backlog which is a list of selected work items for the sprint. We have daily standups and later a sprint review which is an all team meeting where the finished work from the sprint is presented for review.
Whether you’re a patient or a healthcare professional, health and medical apps provide major benefits. They help physicians, pharmacists, psychiatrists, and more improve their workflows to provide an overall faster and better service. They encourage patients to take better care of their health and a more proactive approach to it.
At Hattrick we’re not your average healthcare application development company. We’re a dedicated team of engineers, developers and designers that are committed to helping companies build innovative mobile and web apps that improve people’s lives. If you have a project you’d like to collaborate on, get in touch with us!




