UX/UI design is a big component of software development. It consists of defining, researching, analyzing and designing the product whether physical or digital. Designing with accessibility in mind allows for people with a range of abilities and disabilities to perceive, understand, navigate, interact with, and contribute to the web. On the same wavelength the content that designers create represents our social thought, values, and culture. This is why it’s important to design great products that follow moral principles, also known as ethical design.
If you need to brush up on what the UX/UI process looks like and/or are interested in how it affects healthcare products in particular you can check out our previous post here.
Below we explain all about accessibility and ethical design, why it’s important and why these practices need to be talked about more.
What is UX/UI design
User experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design are concepts that have many dimensions, and it includes various different disciplines such as interaction design, information architecture, visual design, usability, and human-computer interaction. UX design is the process design teams use to build products that provide meaningful and relevant experiences to users, always having them in mind when designing the product. This involves the design of the entire process of acquiring and integrating the product, including aspects of branding, design, usability and function. The goal is to make using these products and/or services easy, logical, and fun.
The User interface (UI) is a part of UX design, it’s the procedure, centered around the user, of designing the aesthetics of a digital product. It’s essentially creating the look and feel of a mobile or web application. An interface is the graphical layout of the application. The goal is to make the interface functional and easy to use while simultaneously being visually appealing. In UI design designers are focused on the visual elements that let users interact with a product, not so much with the experience they will have with it. Examples of things taken into account during UI design are color palettes, typography, buttons, animation, and other imagery.
Why is UX/UI important in software development
A meaningful user experience allows companies to define customer journeys on their product that are most conducive to business success. Some key points in favor of UX/UI design are:
- Increase customer loyalty and retention: UX design is first and foremost about users' emotions and feelings. Which is why it can have a long-term impact on user behavior. If users find the product helpful, pleasant, easy to use and have positive experiences with it, they will continue coming back to it.
- Fosters conversion and ROI: A good UX strategy increases return on investment (ROI) due to small improvements that create major impact. To provide a few examples, good UX leads to improved customer retention, more customer recommendations, additional repeat customers, higher conversion rates, and enhanced credibility.
- Investing in UX can reduce costs later: based on research, analysis, and testing, so you are immediately putting the end-user first when developing a product or service and before making other necessary adjustments. Companies that take a UX approach will prevent possible usability issues or problems from the start thus saving money in the long run.
- More efficient user journeys: As for users it aims to fulfill their needs and create a better customer satisfaction conversion retention journey. It’s all about finding a balance between aesthetics and functionality. A well thought out UX design helps end-users be more efficient by allowing them to complete tasks faster, it facilitates the user flow through your product.
What is ethical design
Racial and gender biases often result from unconscious UX design decisions. Everyone has certain biases rooted in them and designers aren’t exempt from that. We’d like to believe that the biases that occur in some design solutions and content aren’t deliberate. The people designing them sometimes just don’t consciously adopt an empathetic mind. The intent of a UX designer to design great products that follow moral principles is known as ethical design. The question of ethical design is something that’s relevant for all products and services. It basically means making conscious design decisions that do good and do not harm anyone, either intentionally or unintentionally.
Ethics is based on well-founded standards of right and wrong that advise what humans should do, usually in terms of rights, obligations, benefits to society, fairness, or specific virtues. Consistently applying a moral code when making design decisions requires subtle perceptions of right and wrong on the designer’s part. This can range from choosing the skin colors for emojis to common visual metaphors, every wrong design decision can demean certain people, depending on their gender, race, religion, language, or other dimensions of diversity.
The main areas on which designers should focus to apply ethical design in UX are
- Usability: This refers to how efficiently and satisfactorily a user can accomplish a specific goal, use a particular feature, design solution, or product. You should design interactive user interfaces that are easy to use.
- Privacy: This is one of the main concerns in ethical design. User data has not remained personal and companies and organizations have access to plenty of private data. Designers are responsible for using this information appropriately.
- Influence: Influencing user behavior and their thought process is an important component. Certain persuasion tactics that change users’ perspectives and convince them to buy something just to increase conversions are not very ethical.
- Sustainability: Keeping the environment, climate change and natural resources in mind when designing a product. This is important in order to foster sustainable consumption.
- Society: Aligning the design with the needs of global and local communities, politics, economies, and people’s health.
Best ethical design practices
There are a few main principles to keep in mind when designing products ethically. To ensure that a design is ethical, we could refer to the ‘Ethical Hierarchy of Needs’ pyramid created by Aral Balkan and Laura Kalbag
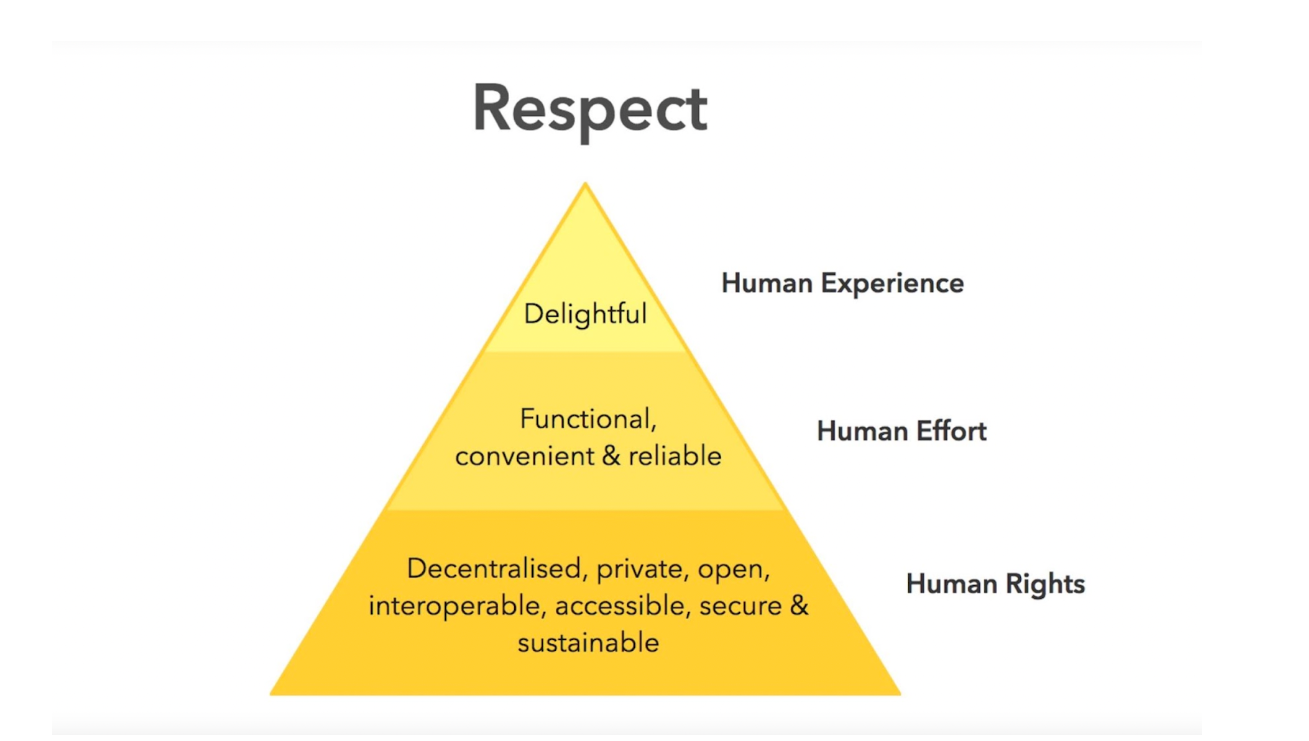
According to the Ethical Hierarchy of Needs, if any of the layers are unfulfilled, the pyramid will collapse. Credit: 99designs
Each level of the pyramid rests on the layer(s) below it. Hence the respect of human rights constitutes the fundamental principle that all design considered ethical should conform to. Moving on up we have respect for human effort and delight in use.
Usability
Usability is, or should be, a basic requirement and an unusable product should be considered a design failure. The design should help the user accomplish what they want, meet their needs, and be easy and pleasant to use. The five quality components of usability according to the Nielsen Norman Group are:
- Learnability: How easy is it for users to accomplish basic tasks the first time they encounter the design?
- Efficiency: Once users have learned the design, how quickly can they perform tasks?
- Memorability: When users return to the design after a period of not using it, how easily can they reestablish proficiency?
- Errors: How many errors do users make, how severe are these errors, and how easily can they recover from the errors?
- Satisfaction: How pleasant is it to use the design?
Privacy
Data security has become a defining issue of our time. Protecting privacy rights aligns with the first level of the Ethical Design Hierarchy of Needs. The level of trust that comes with this respect can elevate the user’s experience to the level of delight. The best ethical design practice would be to develop designs that only collect personal information that is in the best interest of the users. Designers should add features that make it easy for users to modify and delete their data should they want to.
A big example of this is the controversy surrounding Facebook and their data sharing practices. It was revealed that Cambridge Analytica, a British data firm, acquired and sold user data collected from millions of Facebook profiles to US political campaigns. With users becoming increasingly aware of their data privacy rights, websites have become more transparent and cautious about what kind of data they keep and what they do with it.
When users don’t trust a website’s security or integrity, they will likely avoid using it altogether.
Accessibility
Accessibility is a measurement of a user’s ability to use products/services, the extent to and ease with which they can meet their goals. Even though products are always designed for the “targeted customer”, accessibility should be incorporated in the development process of any product or service being built, and not as an afterthought at the end. Designing with accessibility in mind enables people with a range of abilities and disabilities to perceive, understand, navigate, interact with, and contribute to the web.
Accessibility does not mean focusing on users that have some kind of disability. Accessibility design is inclusive of everyone. Maximizing ease of use in order to reach all ability levels leads to products that anyone can use and enjoy, whatever the context. When designing we should keep in mind: touch, sight, hearing, speaking. Barriers that users have can be permanent, temporary or situational. In the instance of sight for example, they can range from people who are completely blind or color blind to those who have low vision.
Apart from increasing the market reach, accessibility features in products and services often solve unanticipated problems. Accessible design also helps a brand’s positioning as one with thoughtfulness towards everyone.
Transparency
It’s a great practice for ethical design to provide transparency so that users can make informed decisions. This includes providing clear ways for users to opt out of memberships and/or subscriptions easily. A clear example of this is Spotify. You can get a free trial to test it out. However, after your free trial is up, Spotify will automatically charge you the monthly fee unless you manually cancel. Being transparent means including a warning or notification before they charge the user.
Sustainability
As we stated above this revolves around keeping the environment, climate change and natural resources in mind when designing a product. This is important in order to foster sustainable consumption. Instead of creating products and services that have a linear lifecycle with a beginning, a middle and an end, the purpose is to design products that are continuously cycled in various forms, following a reuse and recycle loop resulting in less waste. UX and UI professionals should also make pages lighter by providing only the necessary content and optimizing images and photos.
Adopting these principles and practices from the start is a great way to apply ethical design in the UX/UI process. Rather than finishing the process and trying to add more accessible elements or tacking on privacy notification as an afterthought, it’s much easier to start with a clear understanding and intention of these practices.
It’s up to designers and decision makers to uphold ethical-design practices in making all design decisions. They should ensure that no product design or user-interface elements exhibit discriminatory, abusive, or regressive messages or values.




